optomap® Recognizing Pathology
This material is designed as a searchable reference resource to support clinical decision-making. The information contained here should be used as general guidance when viewing optomap and OCT images from Optos devices. The differential diagnosis should be made under the direction of the responsible physician. These images were taken on the latest ultra-widefield optomap devices.
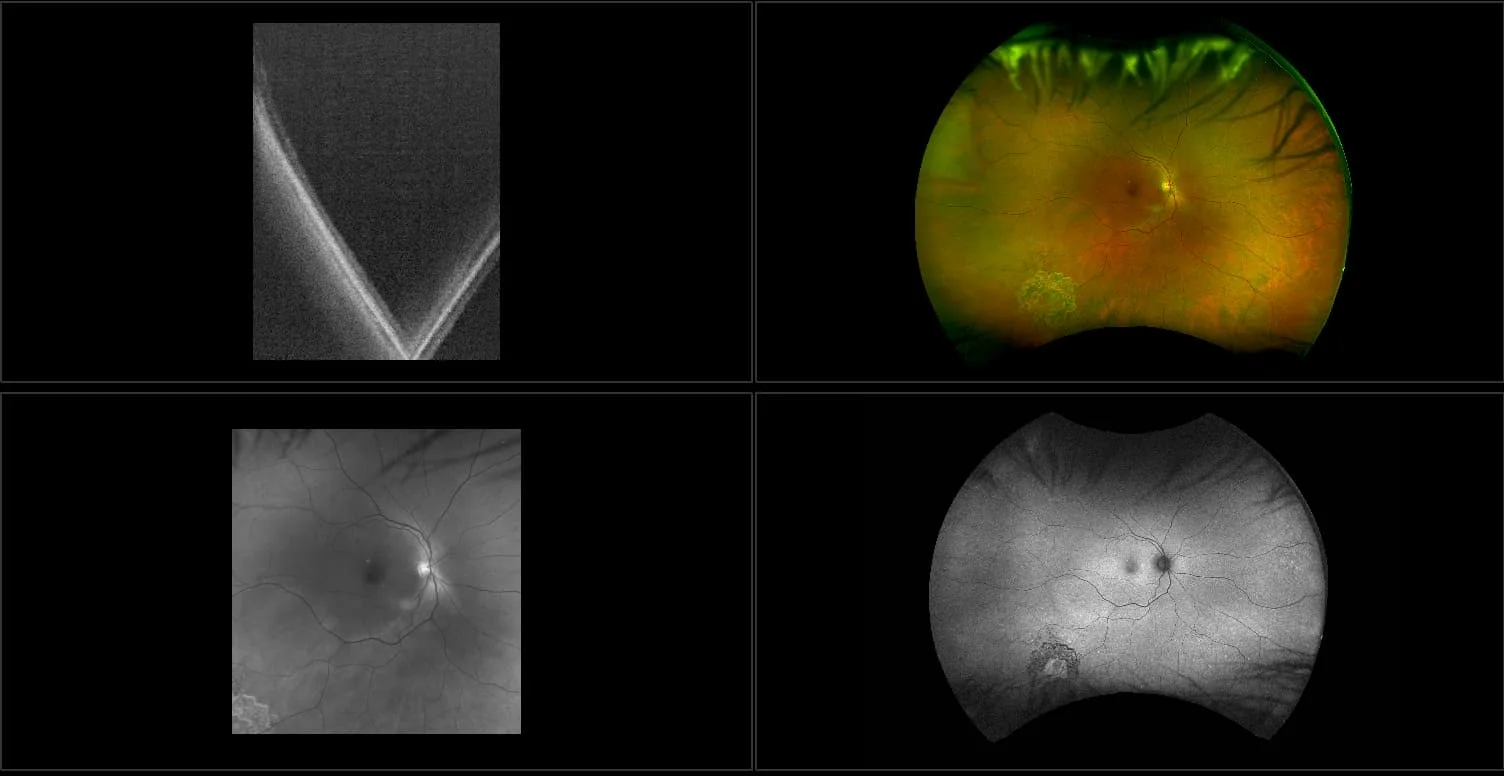
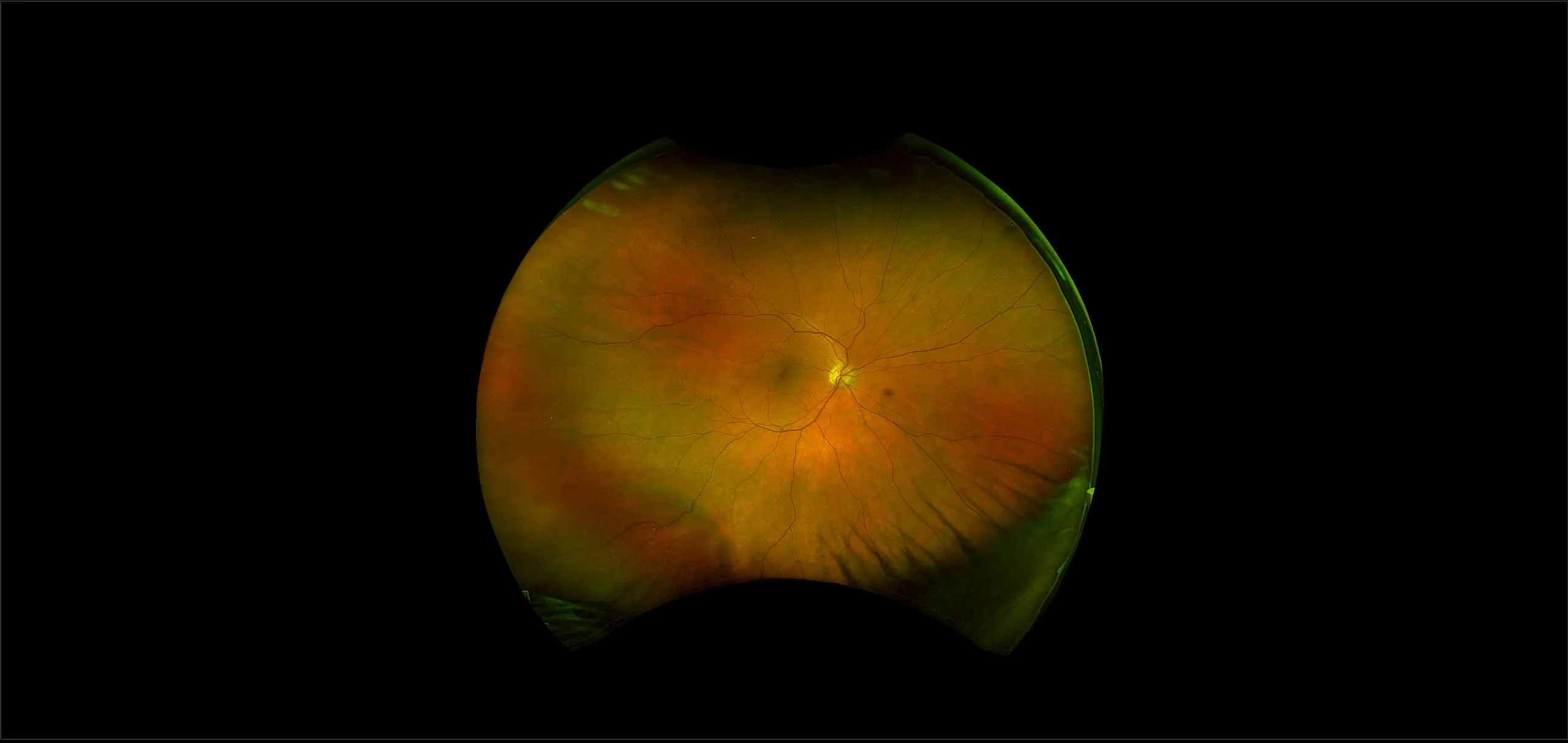
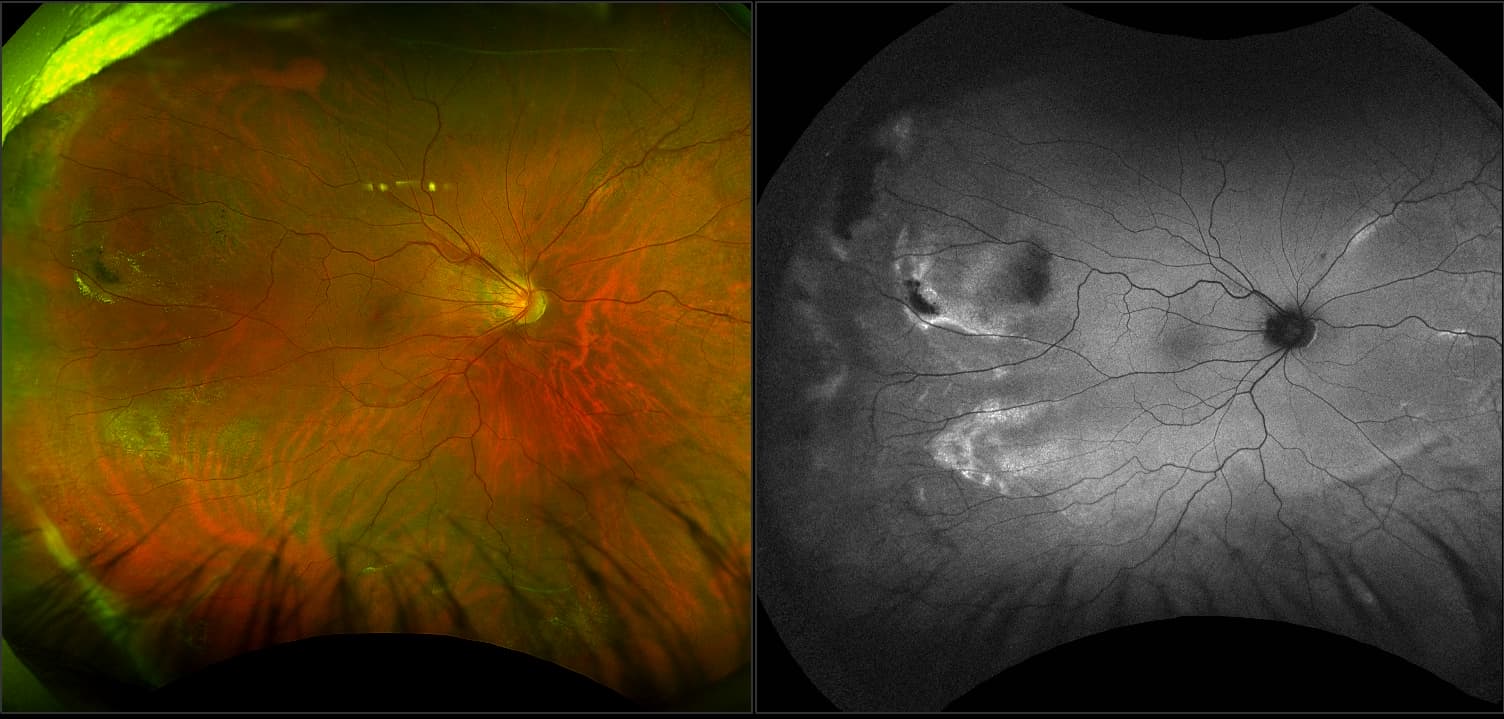
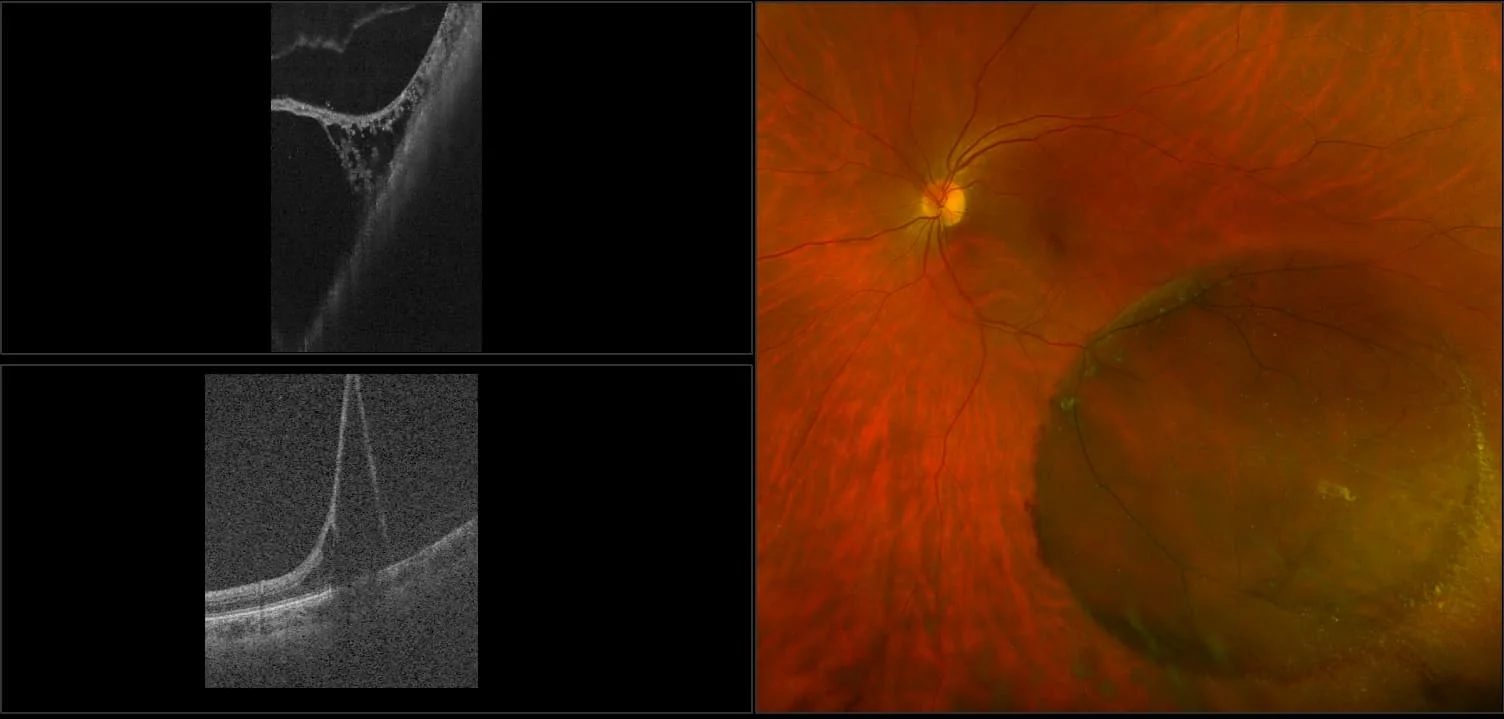
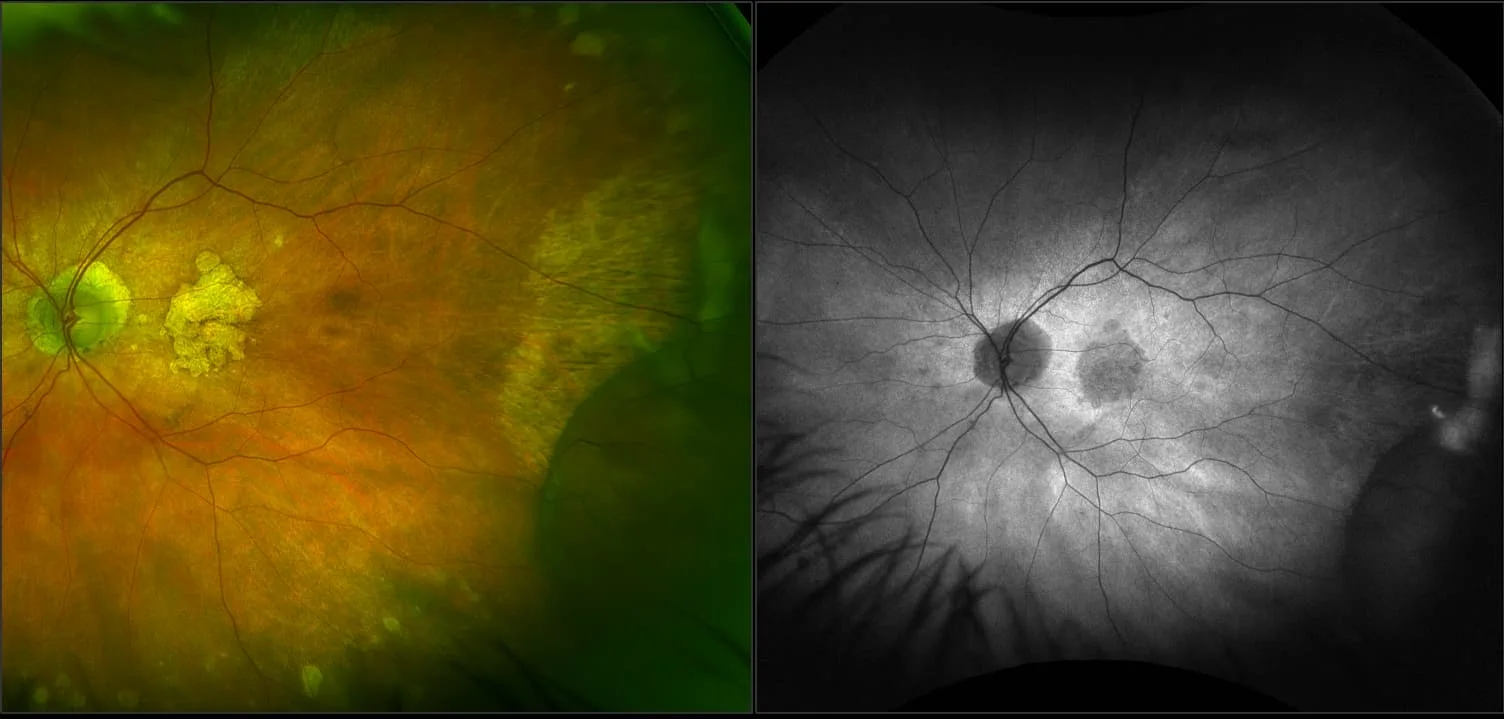
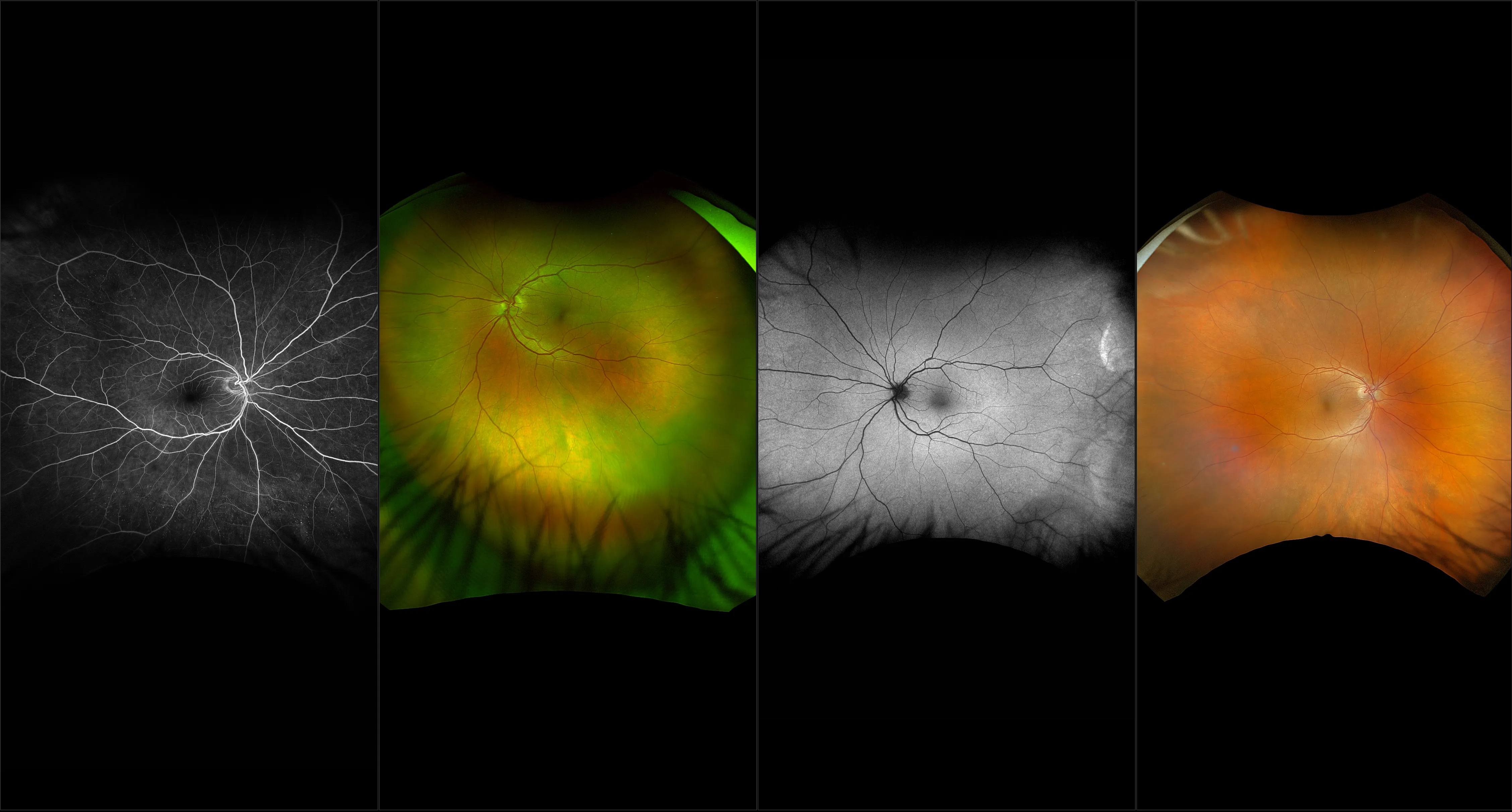
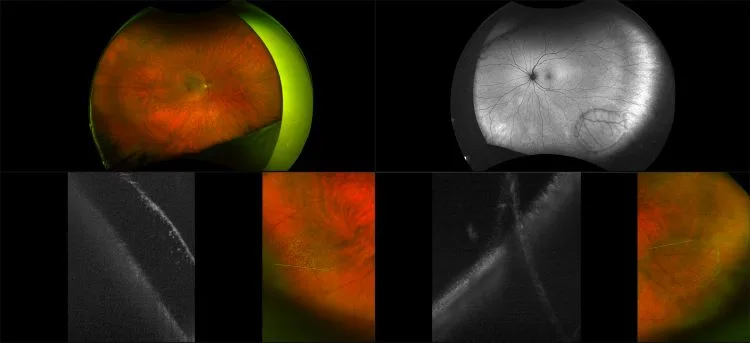
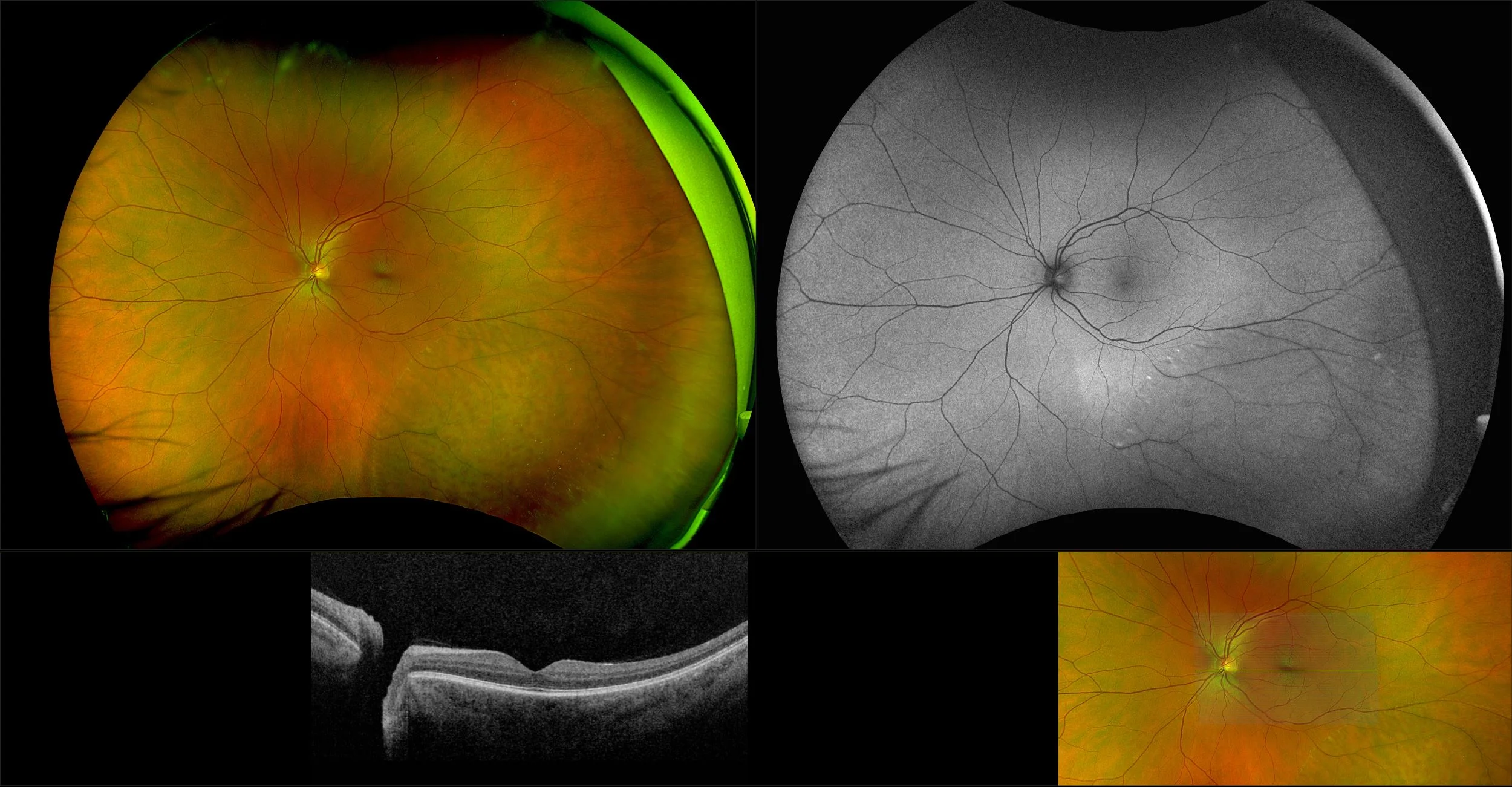
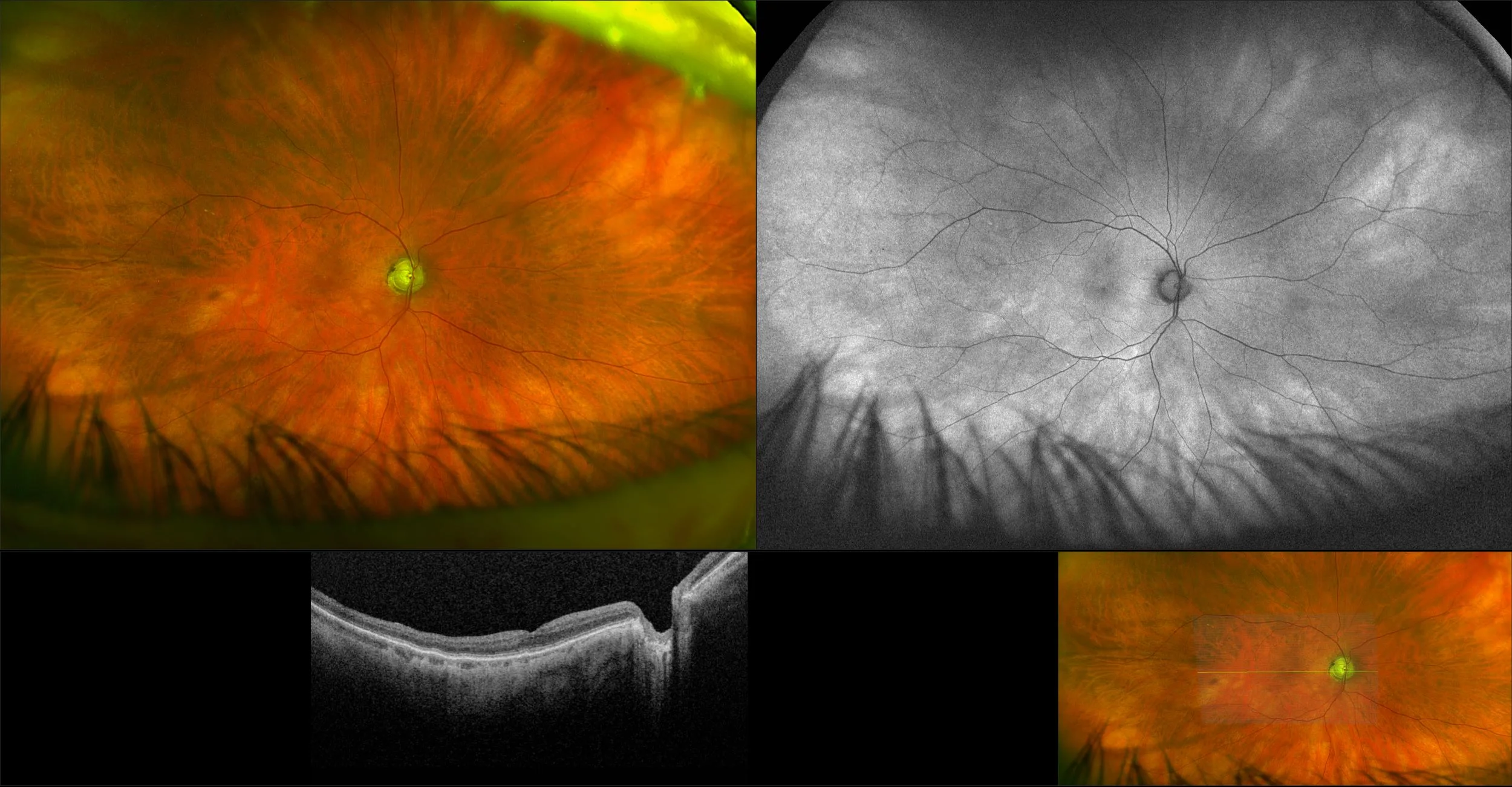
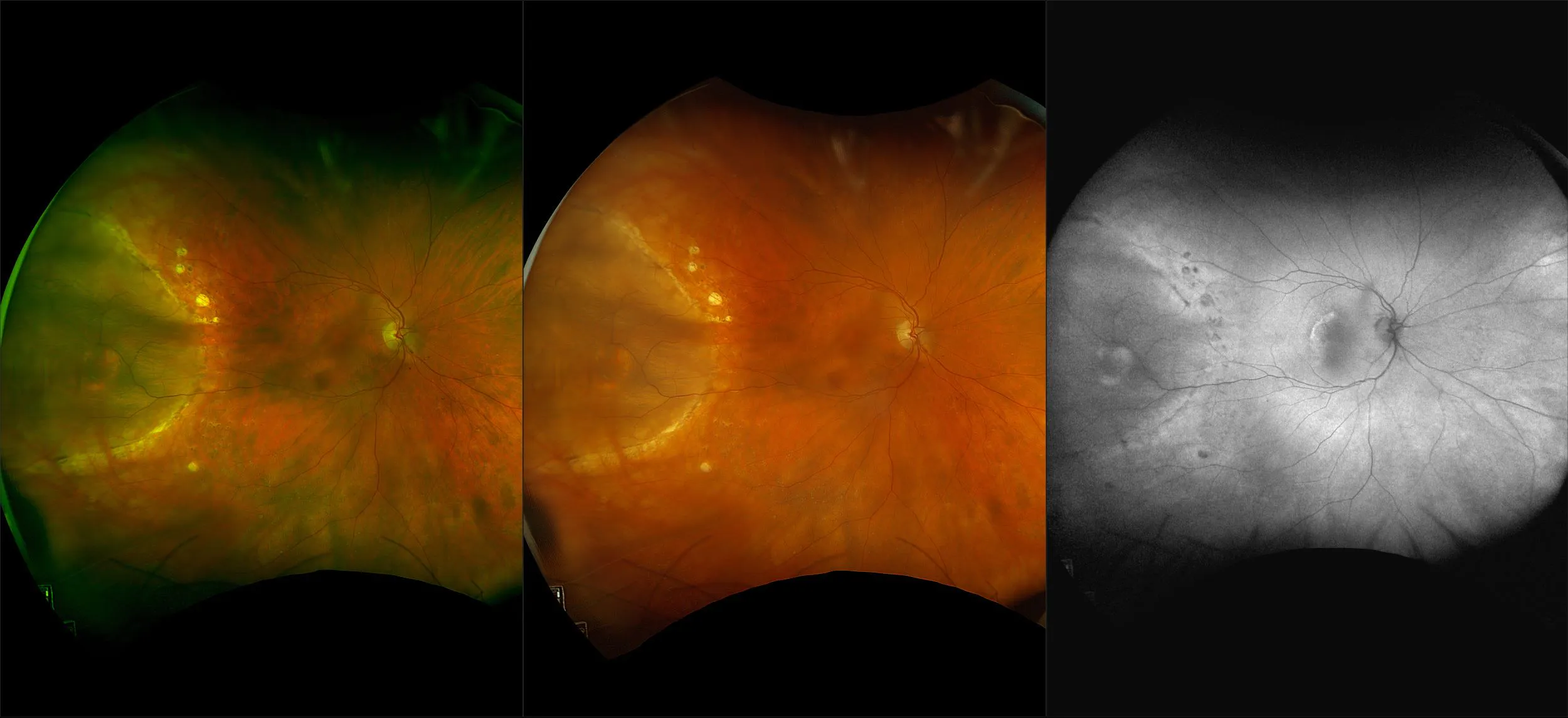
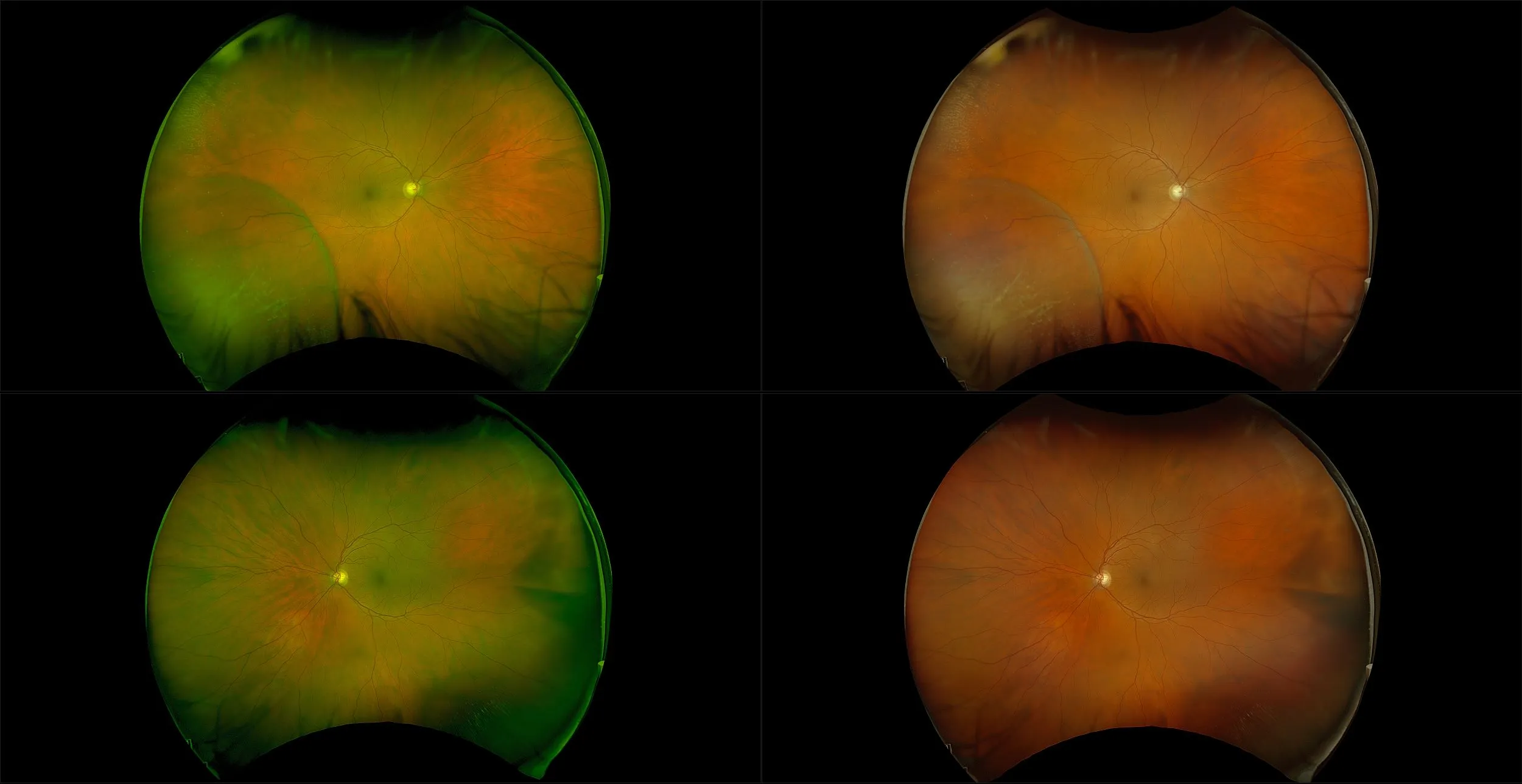
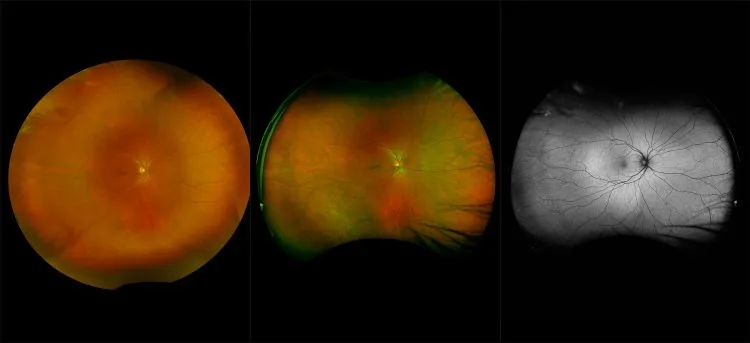
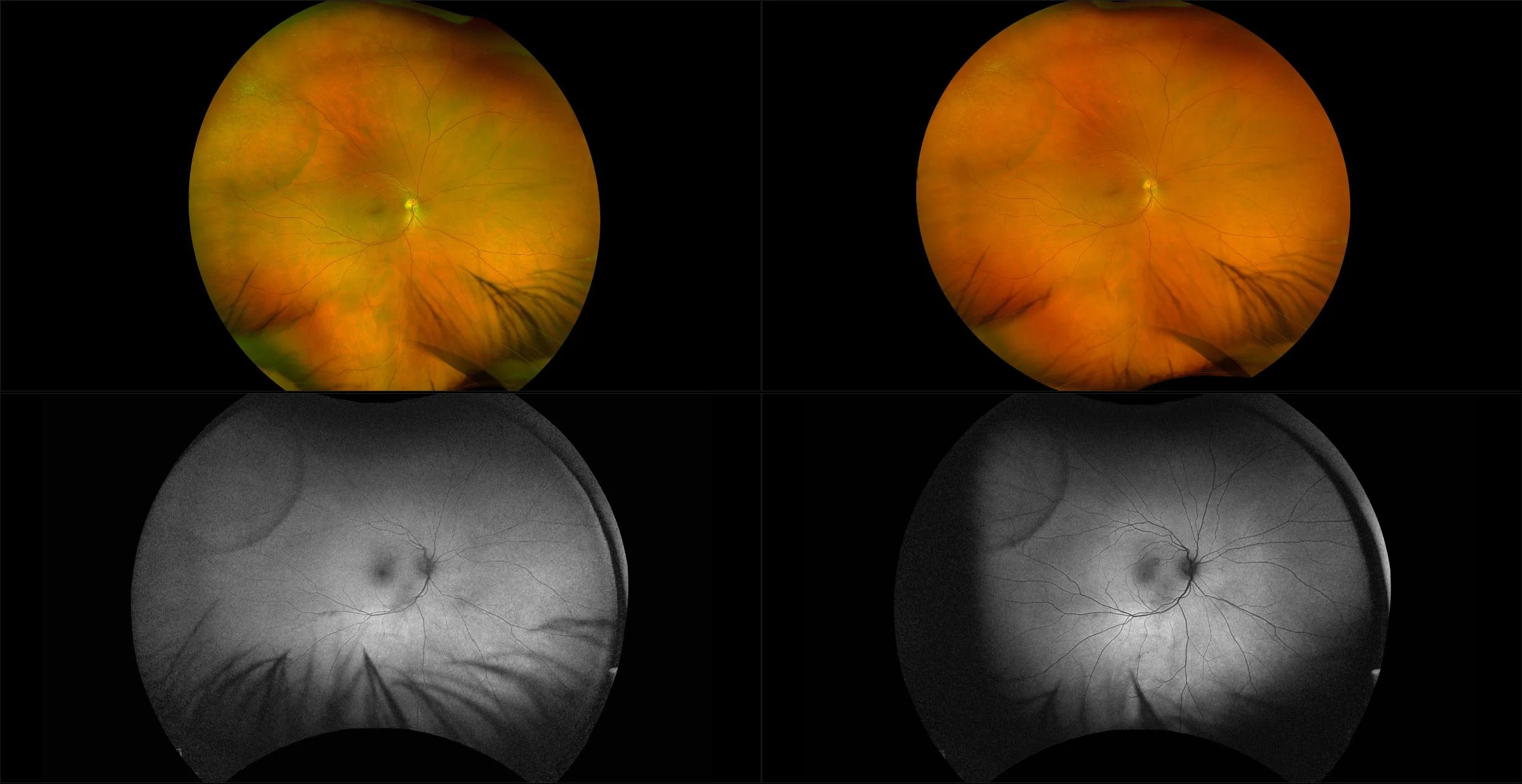
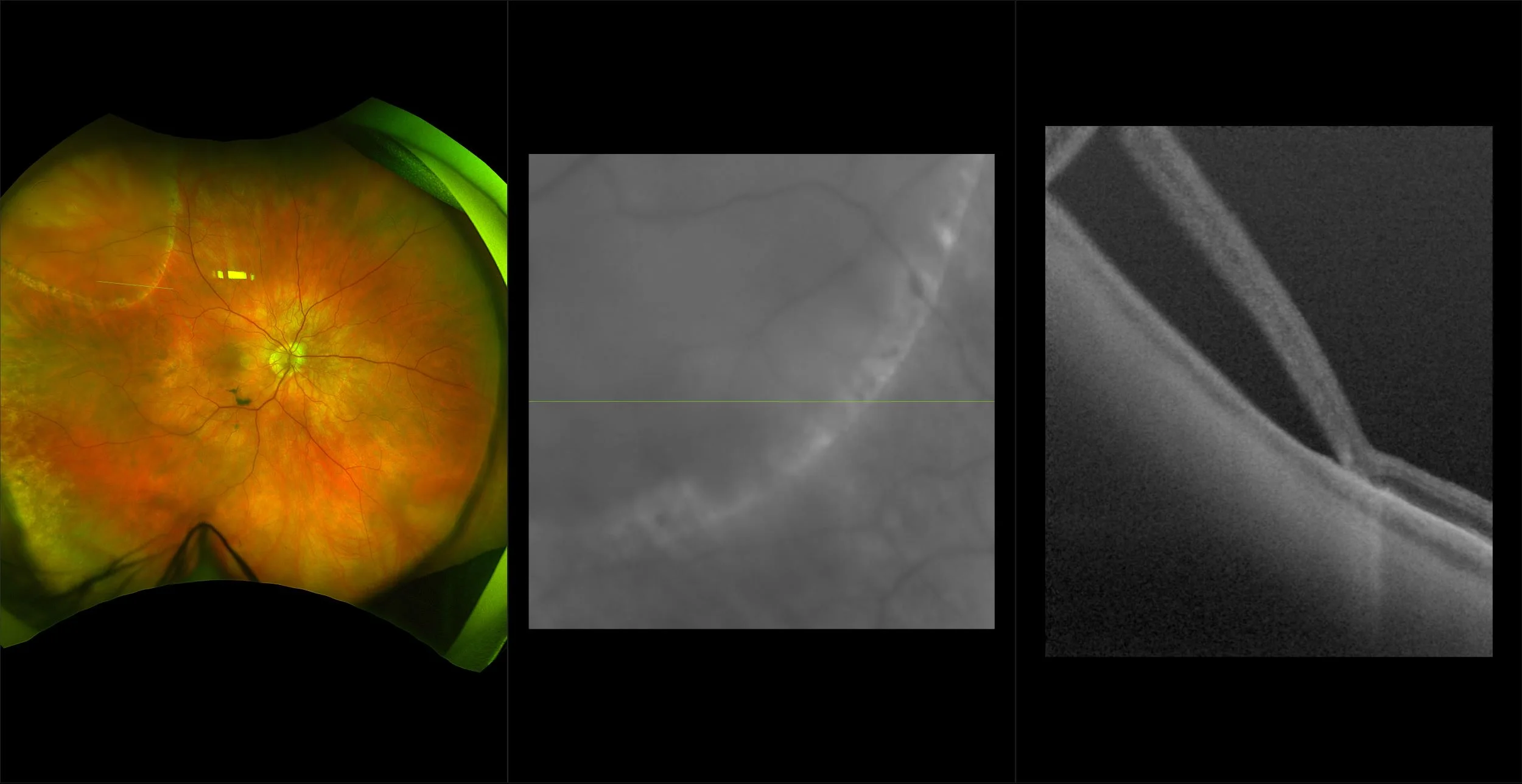
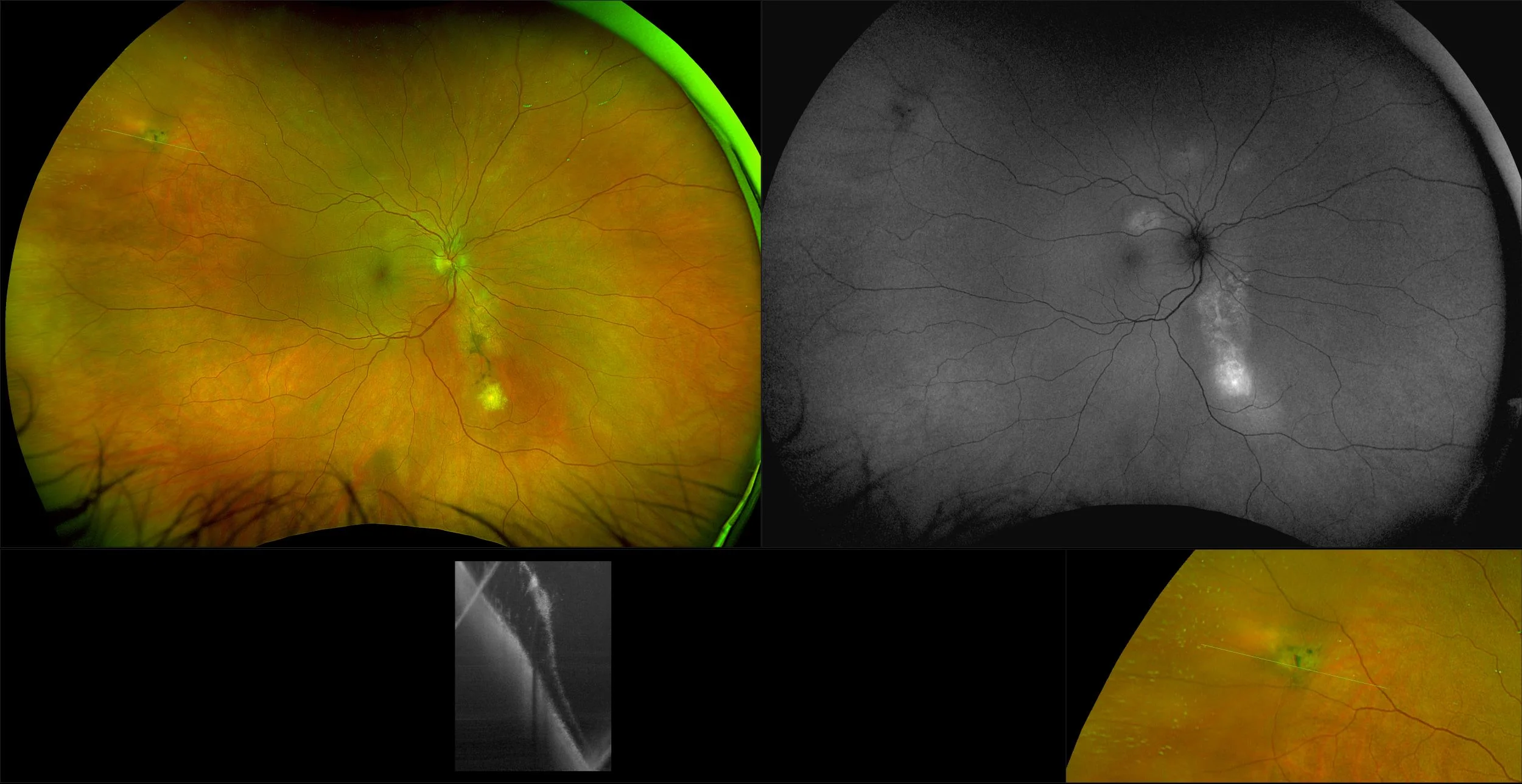
Retinoschisis
A retinoschisis is a splitting of the sensory retina into 2 layers; an inner and outer layer. The etiology is most likely vitreous traction that physically pulls the retina apart. The posterior border of a retinoschisis is convex to the posterior pole, because a retinoschisis forms like blowing up a balloon in the peripheral retina (as seen in most retinal detachments).The inner layer can be shallow or bullous into the vitreous cavity. The inner layer may or may not have retinal vessels in it (depending if the retinal vessels pass into the inner layer or outer layer). Since the vessels in the inner layer are above the retinal surface like vitreous floaters, they can block the exiting light and produce a shadow effect ‘dark vessels’.