optomap® Recognizing Pathology
This material is designed as a searchable reference resource to support clinical decision-making. The information contained here should be used as general guidance when viewing optomap and OCT images from Optos devices. The differential diagnosis should be made under the direction of the responsible physician. These images were taken on the latest ultra-widefield optomap devices.
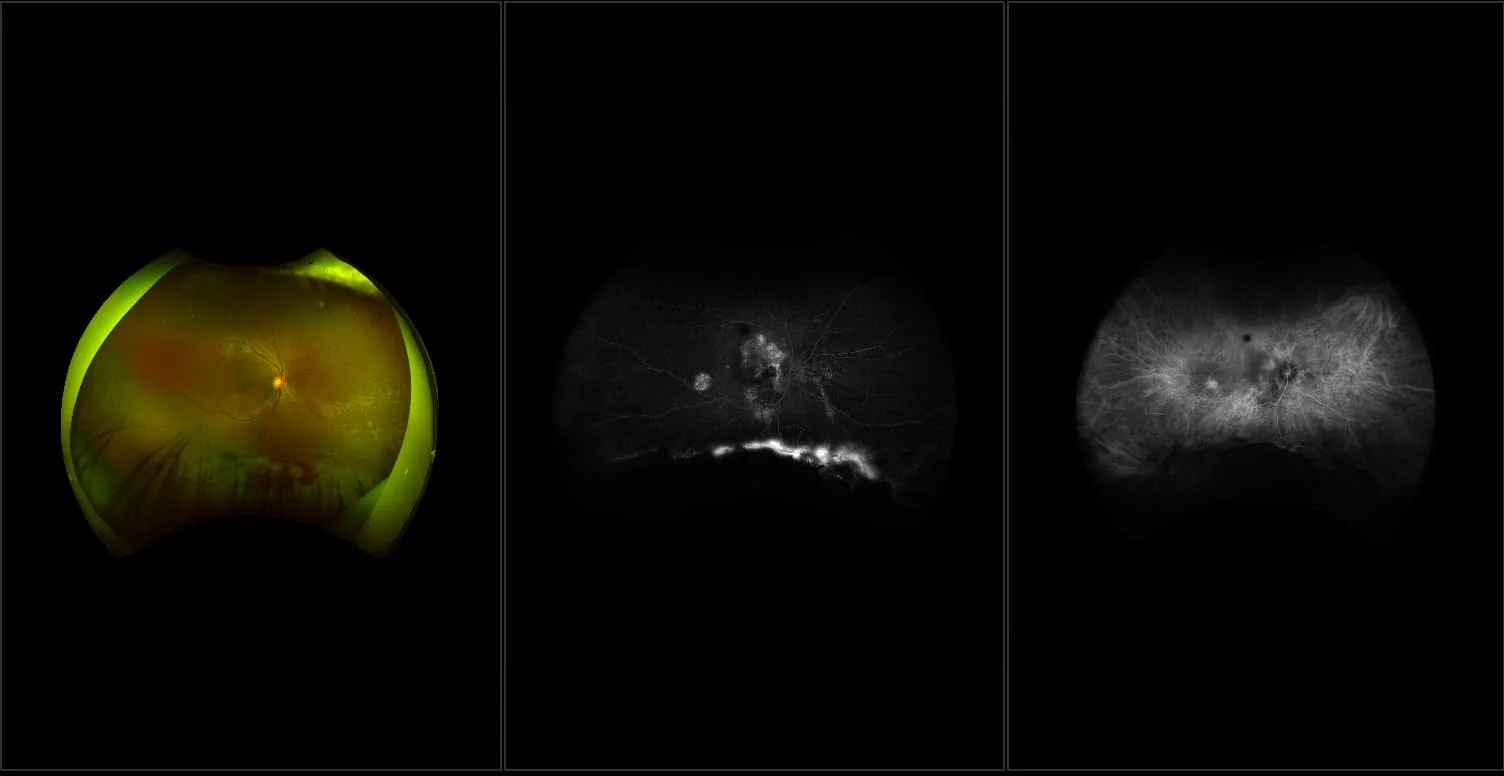
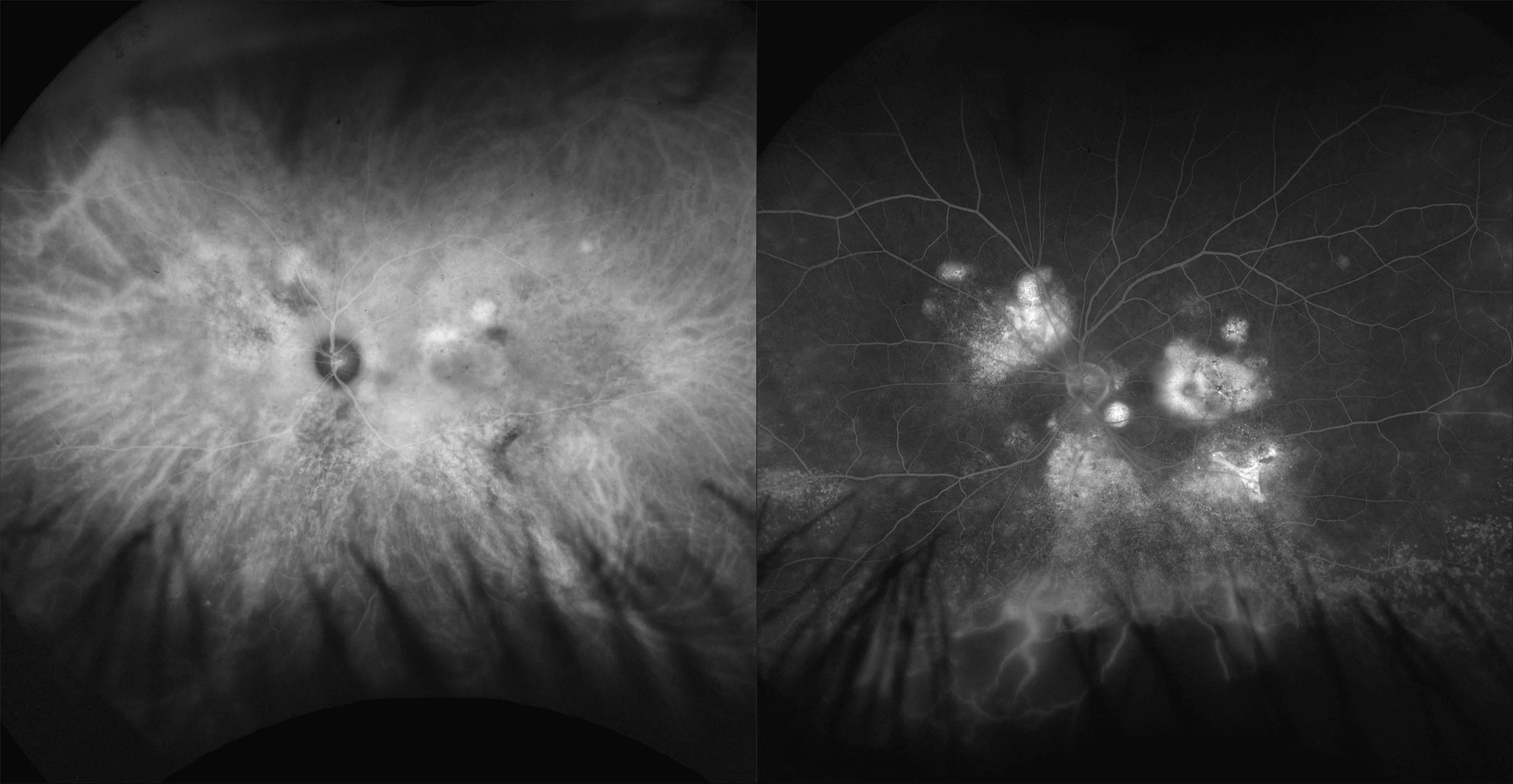
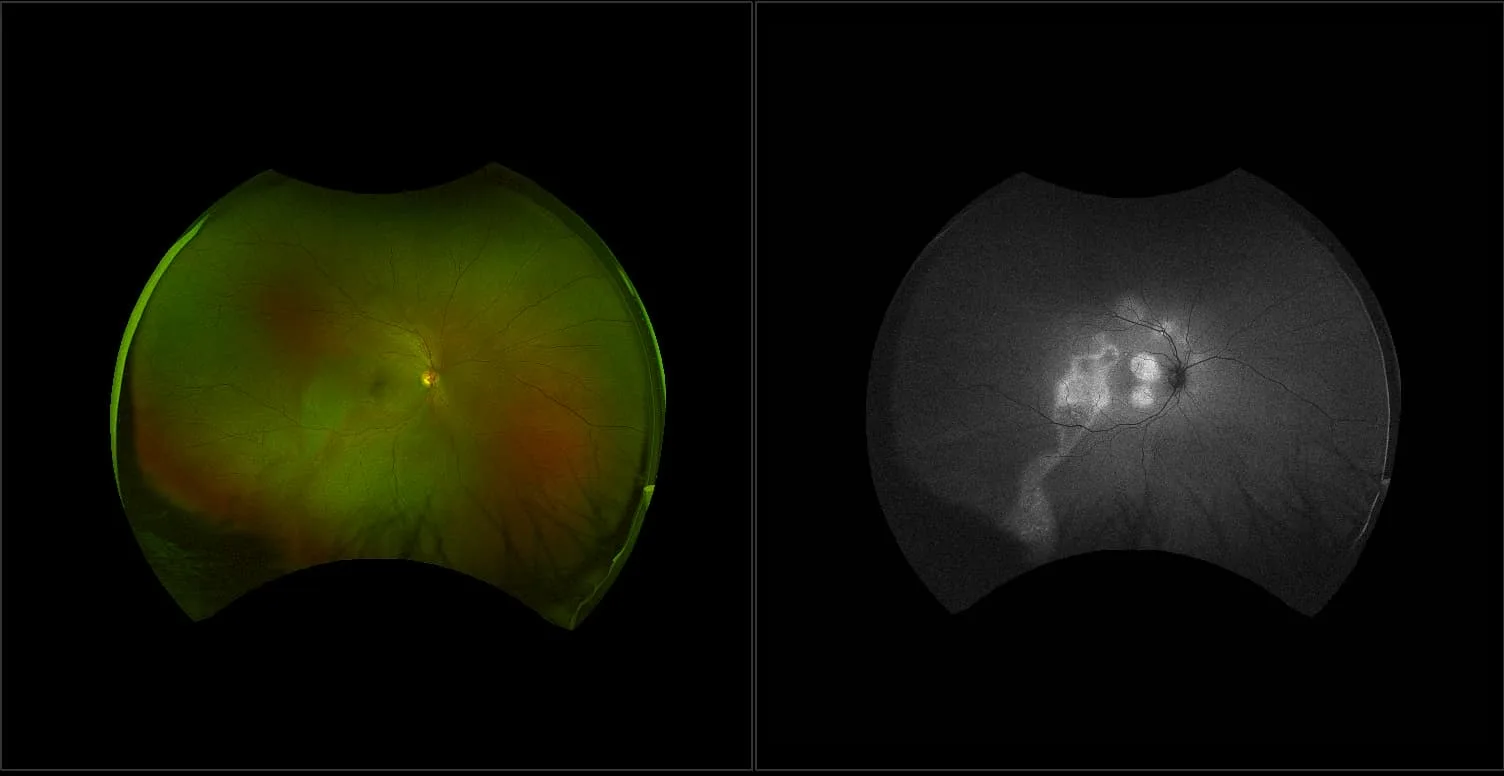
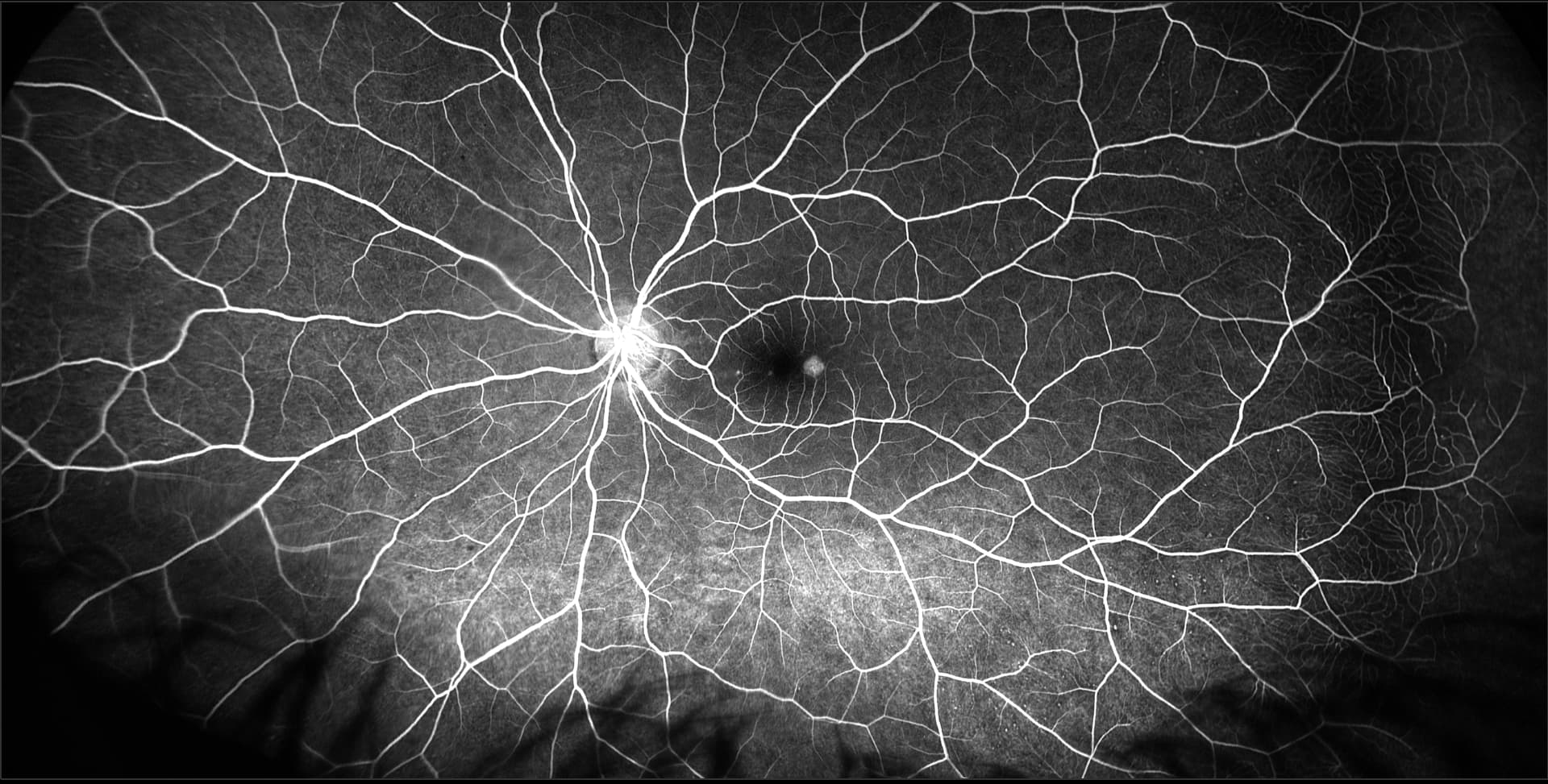
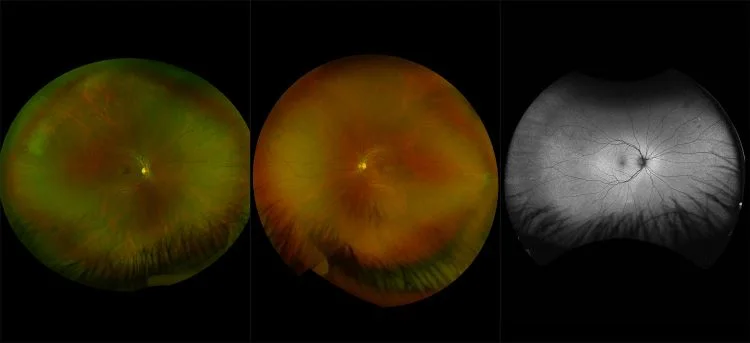
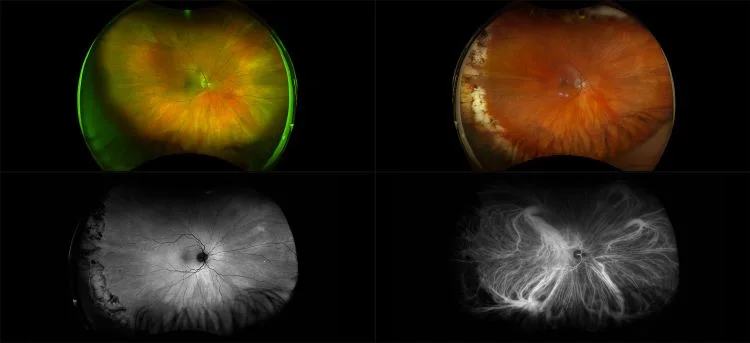
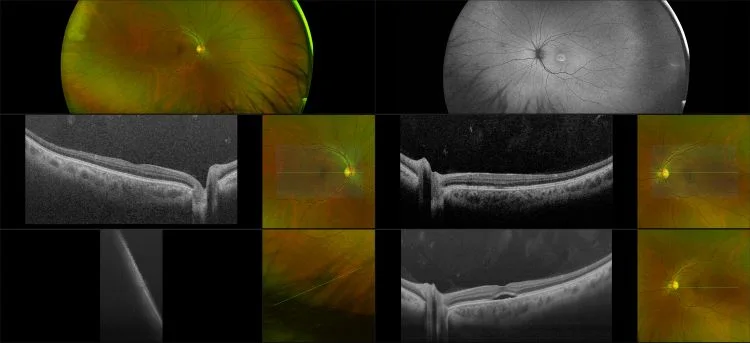
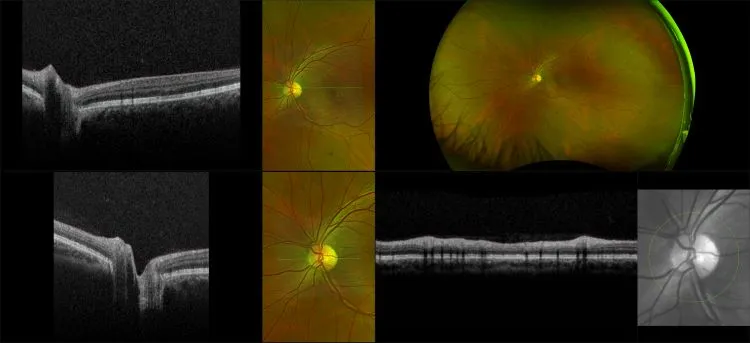
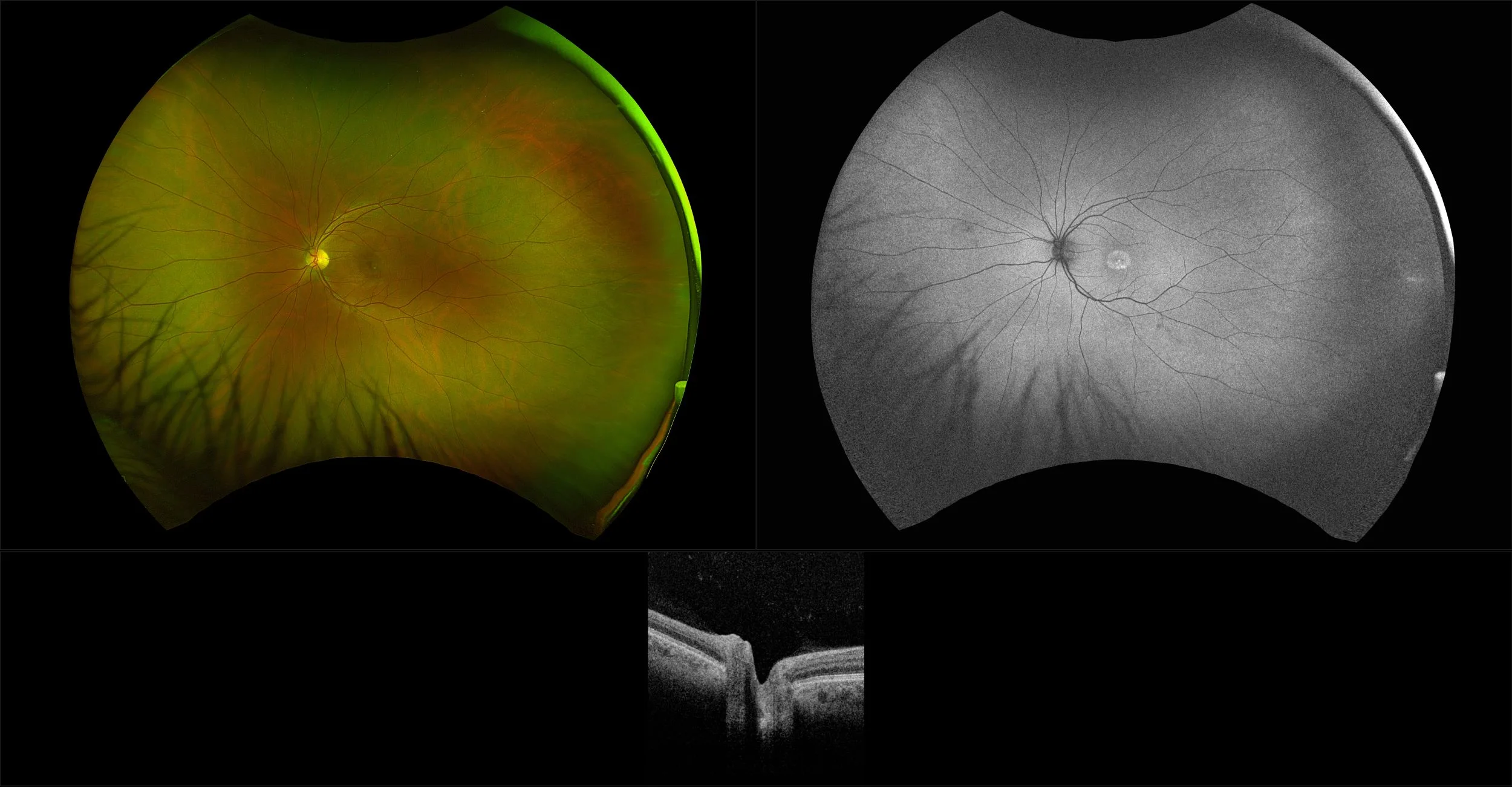
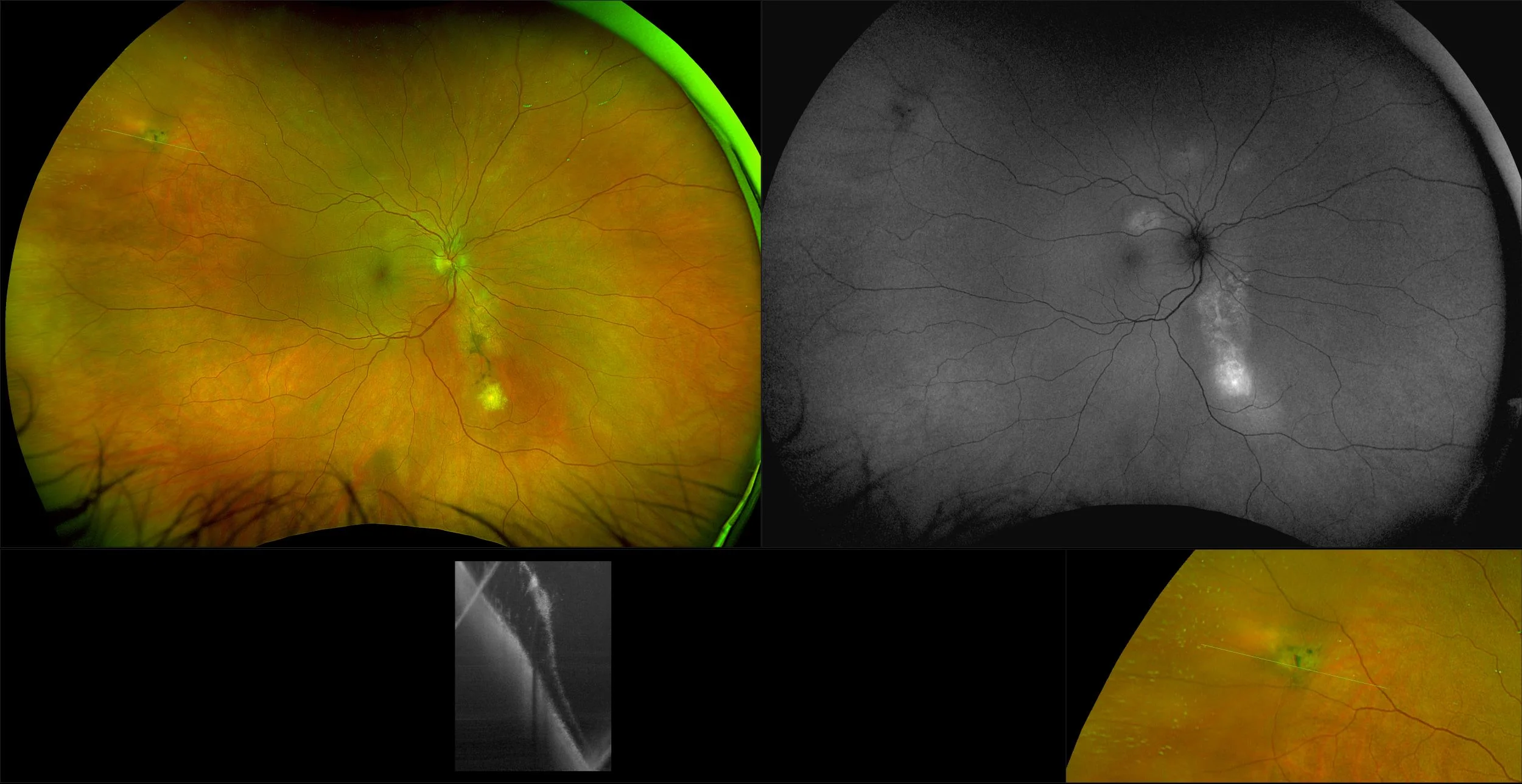
Central Serous Chorioretinopathy
The exact cause of central serous chorioretinopathy is due to venous congestion the choriocapillaris beneath the macular area. The vasospasm results in local ischemia that produces defects in the overlying pigment epithelium. The focal defect in the pigment epithelium causes a breakdown in the zonular occludes tight junctions around the pigment epithelial cells. Loss of the tight junctions permits fluid from the choroid to pass through the pigment epithelial layer and produce a serous detachment of the neurosensory retina.